Medical Imaging
Medical imaging is a set of techniques used to visualize the inside of the human body for diagnostic purposes. The main examinations include X-ray, Ultrasound, MRI, and CT (scanner). Ultrasound uses ultrasound, MRI uses safe magnetic fields, while X-ray and CT use X-rays that require special attention to minimize risks.
The NECIR center strives to comply with radiation protection standards, including exposure limits for both employees and patients, in addition to safety measures recommended by the International Commission on Radiological Protection (ICRP) and the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) to minimize adverse health effects caused by radiation.

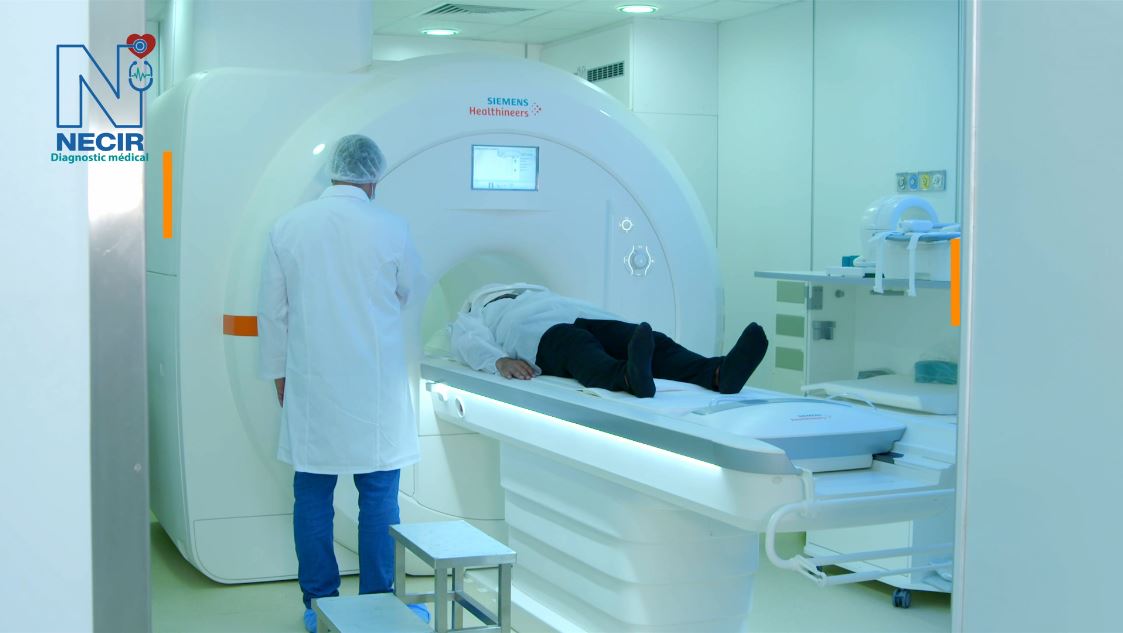
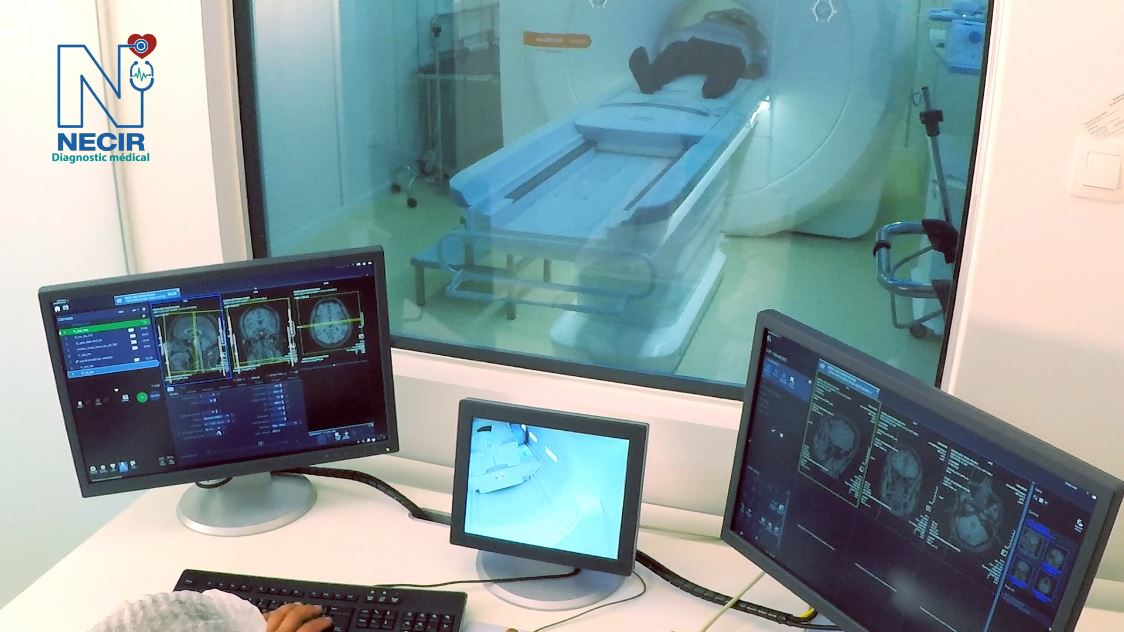
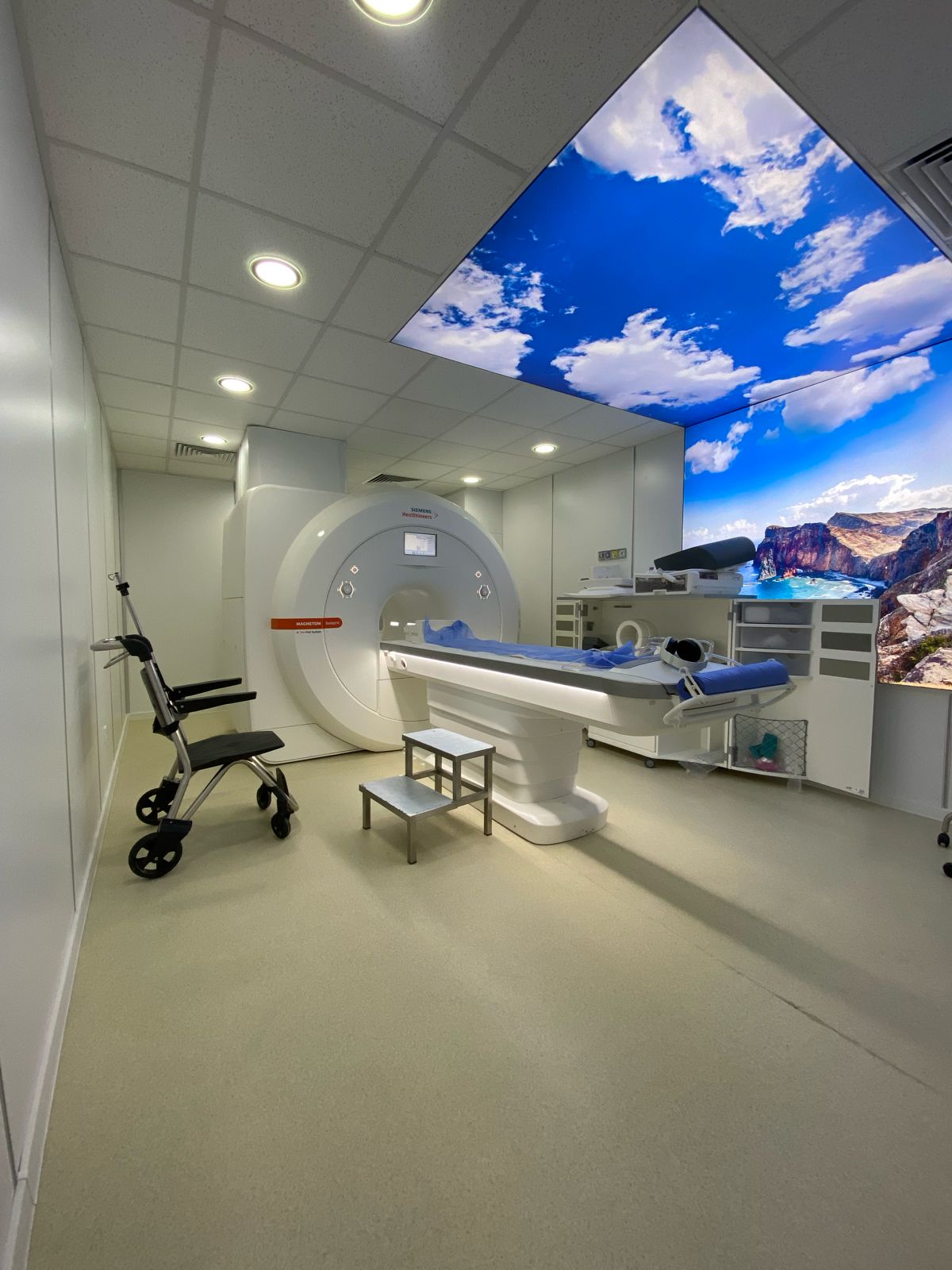
MRI
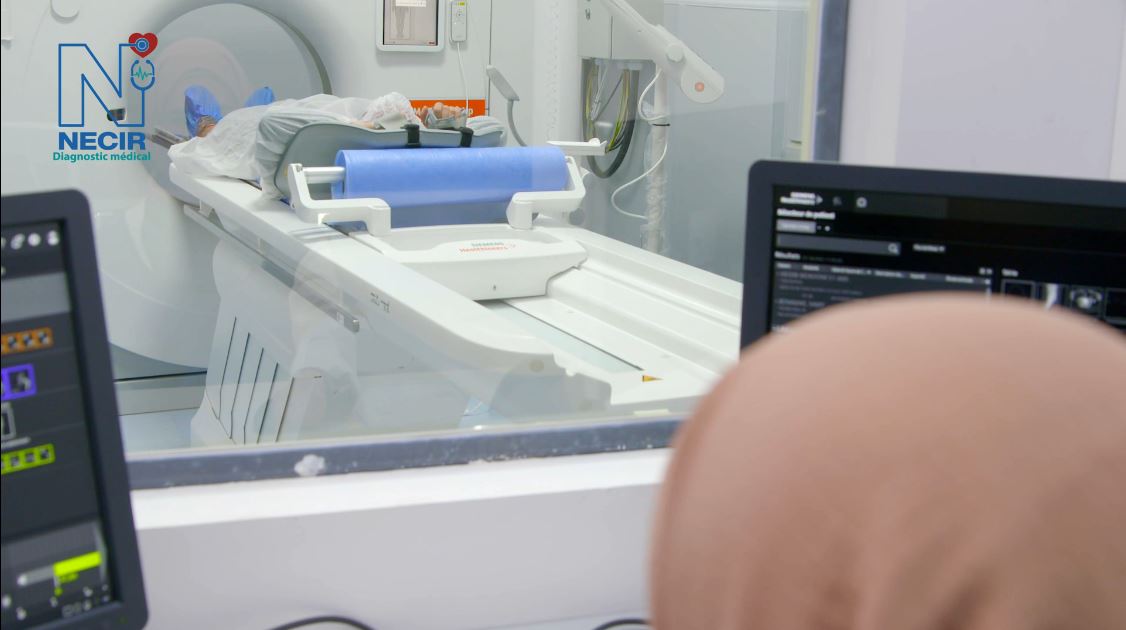
The Siemens Magneton 1.5 Tesla MRI is a magnetic resonance imaging system that delivers high image quality thanks to its powerful 1.5 Tesla magnetic field. It is designed for various clinical applications, offering optimized spatial and temporal resolution for fast and accurate examinations. Its compact design and energy efficiency make it a popular choice for medical centers.

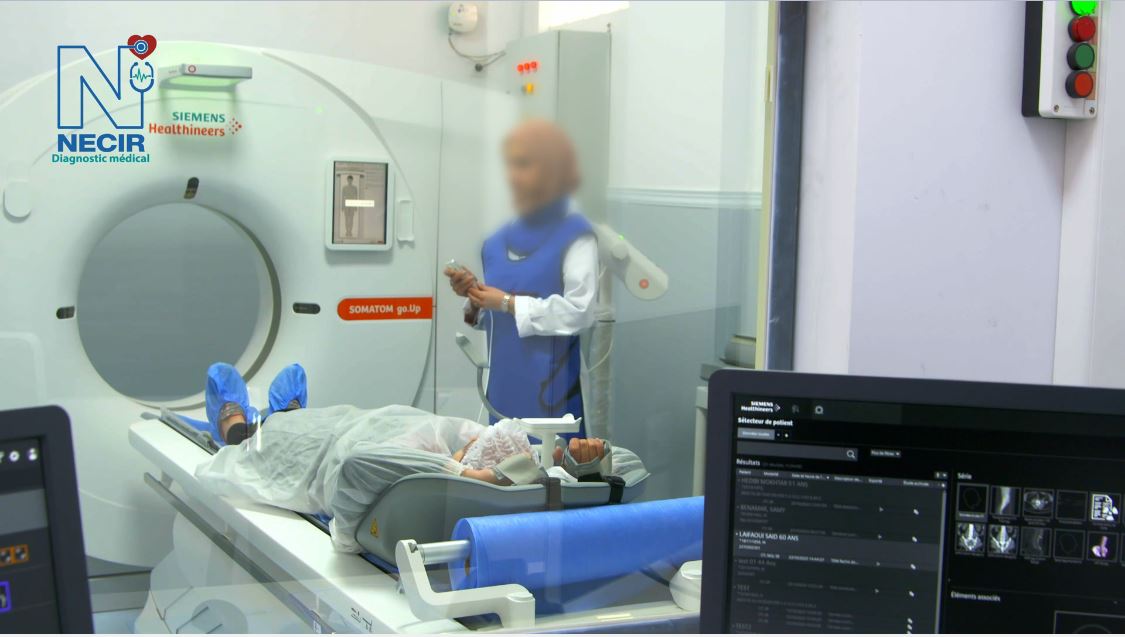
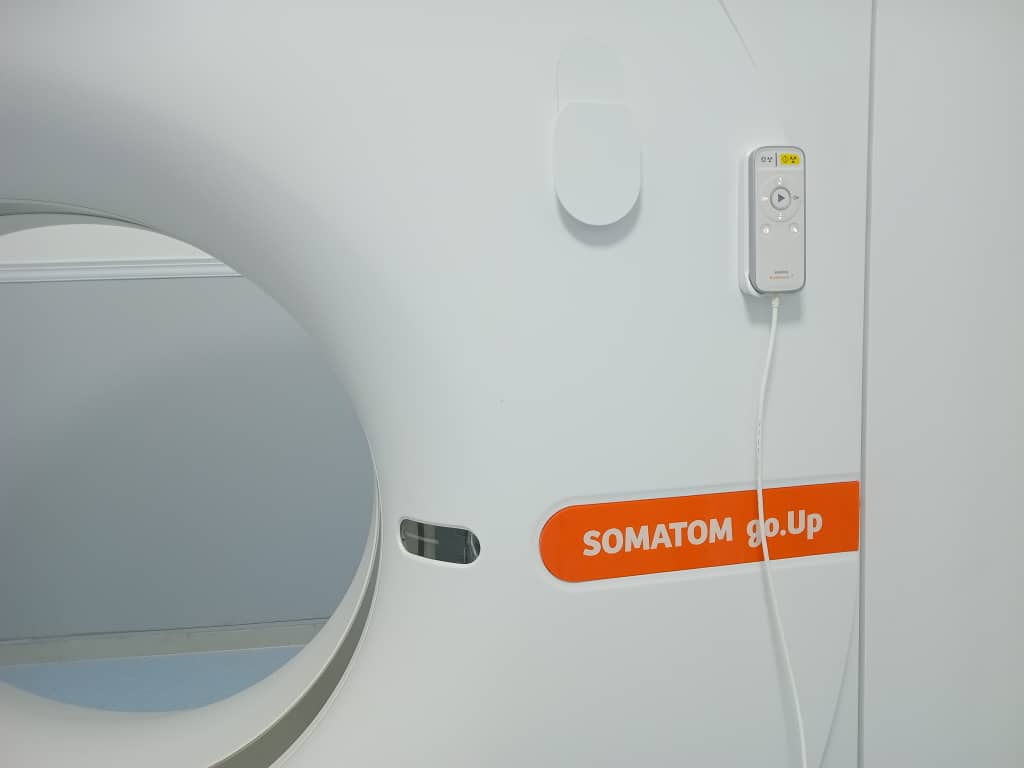
CT Scanner
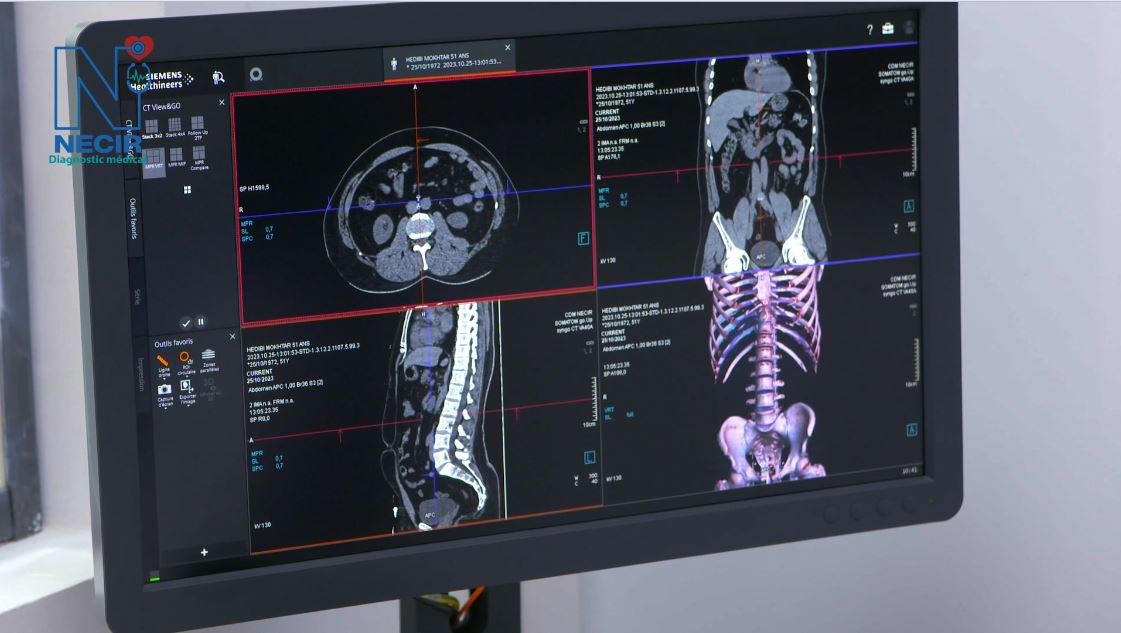
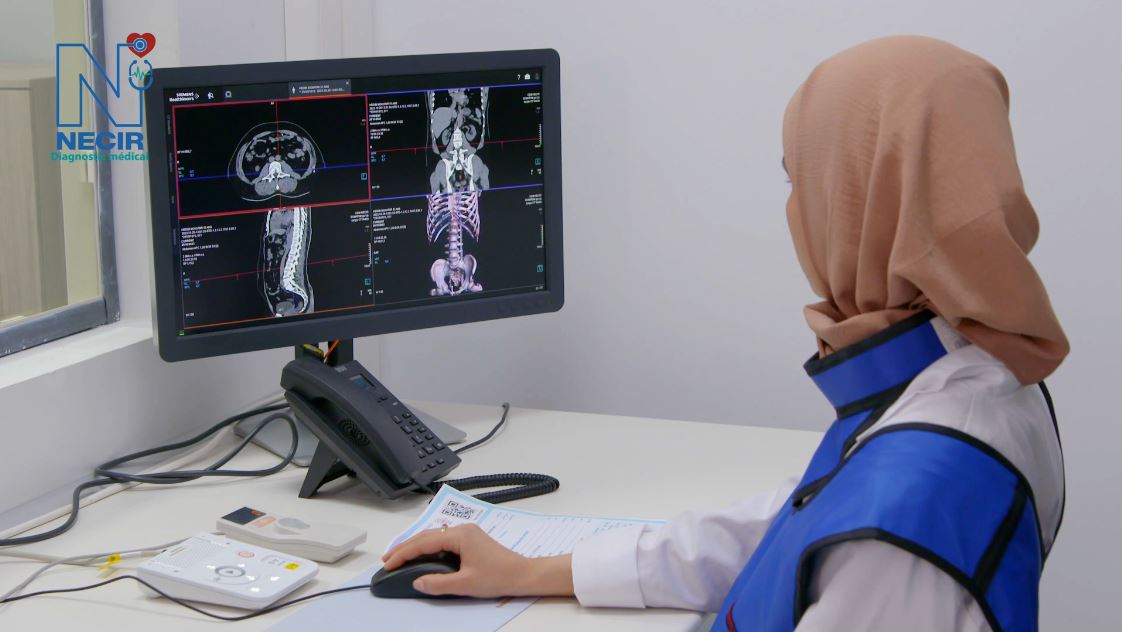
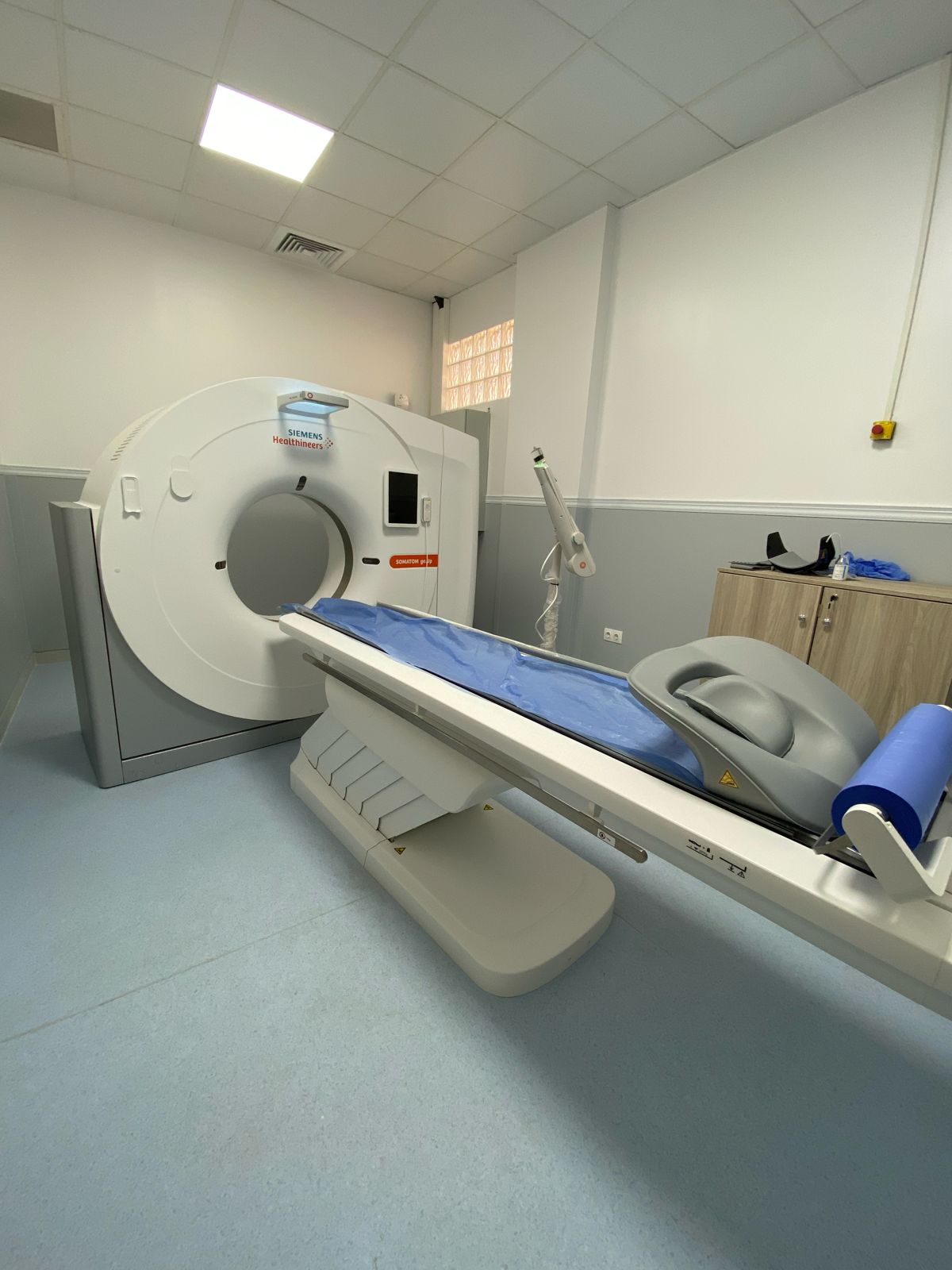
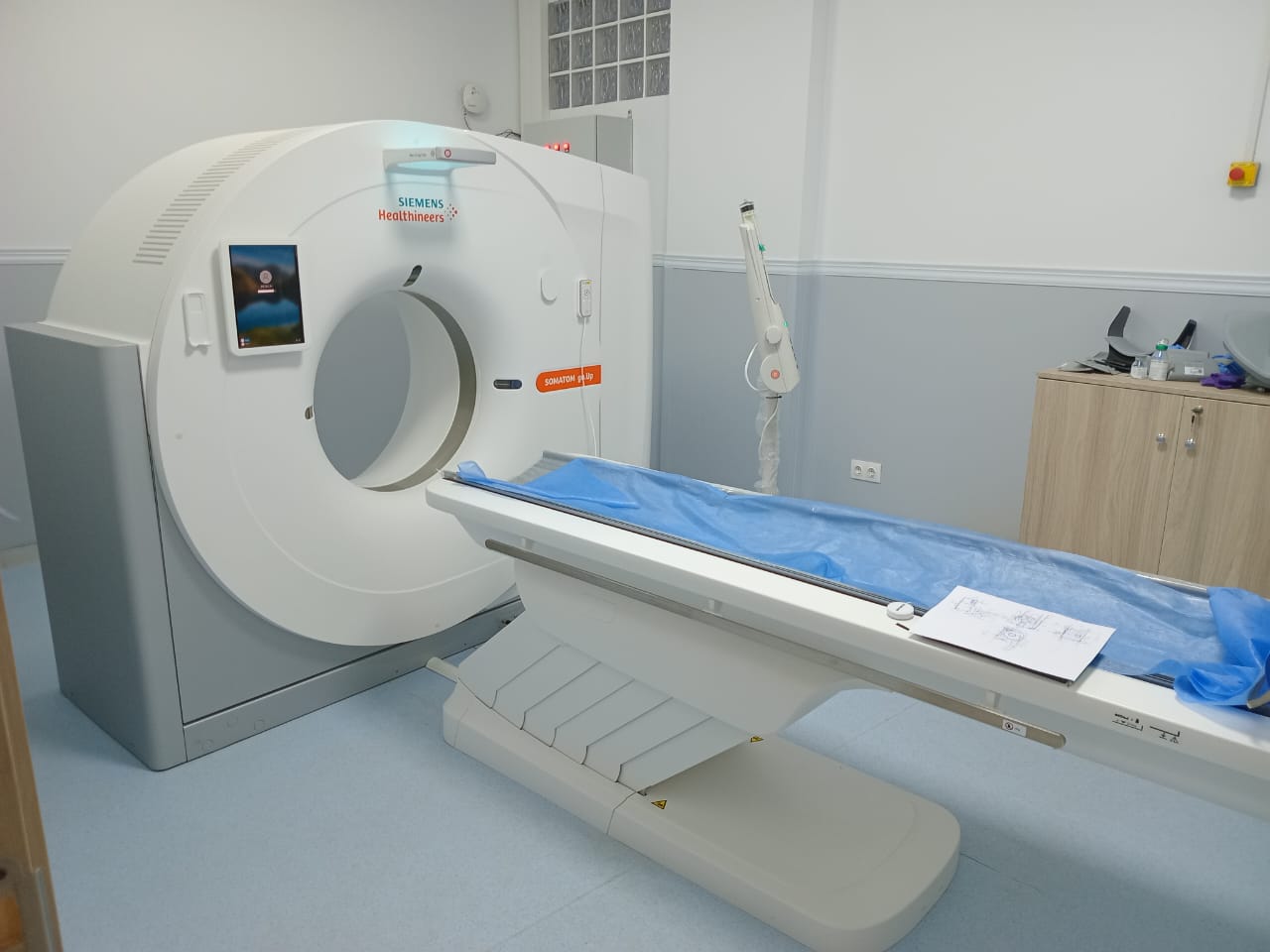
Thanks to its cutting-edge technology, the SOMATOM Go.Up SCANNER transforms complex examinations into fast and efficient routine examinations, which remains essential in the context of patient radiation protection, as its technology allows the scanning of large acquisition areas while maintaining high spatial resolution.

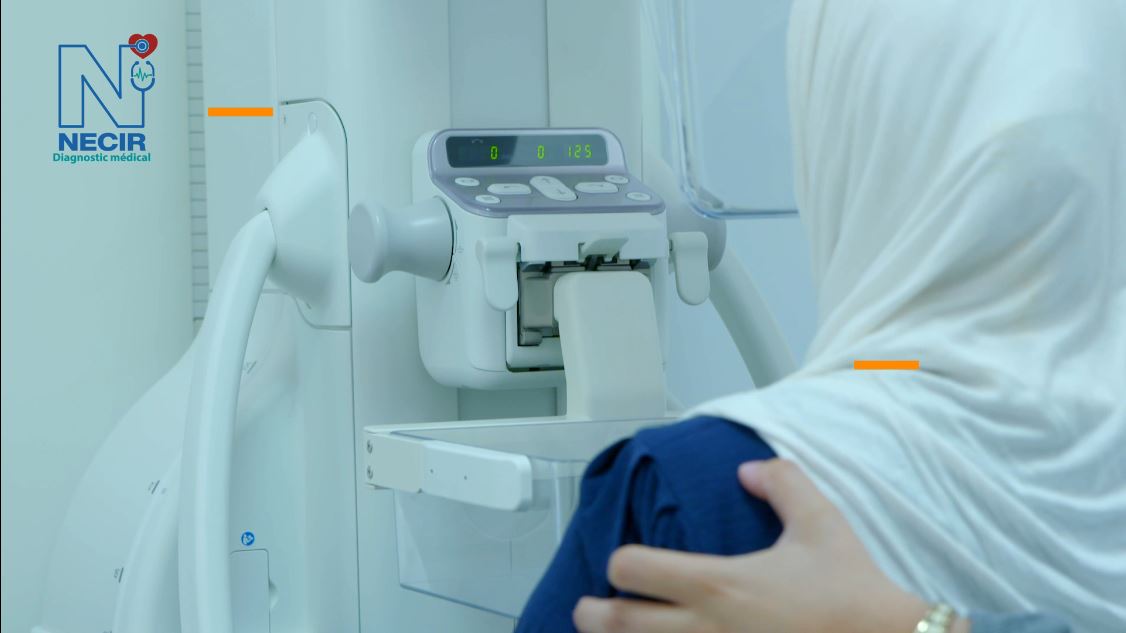
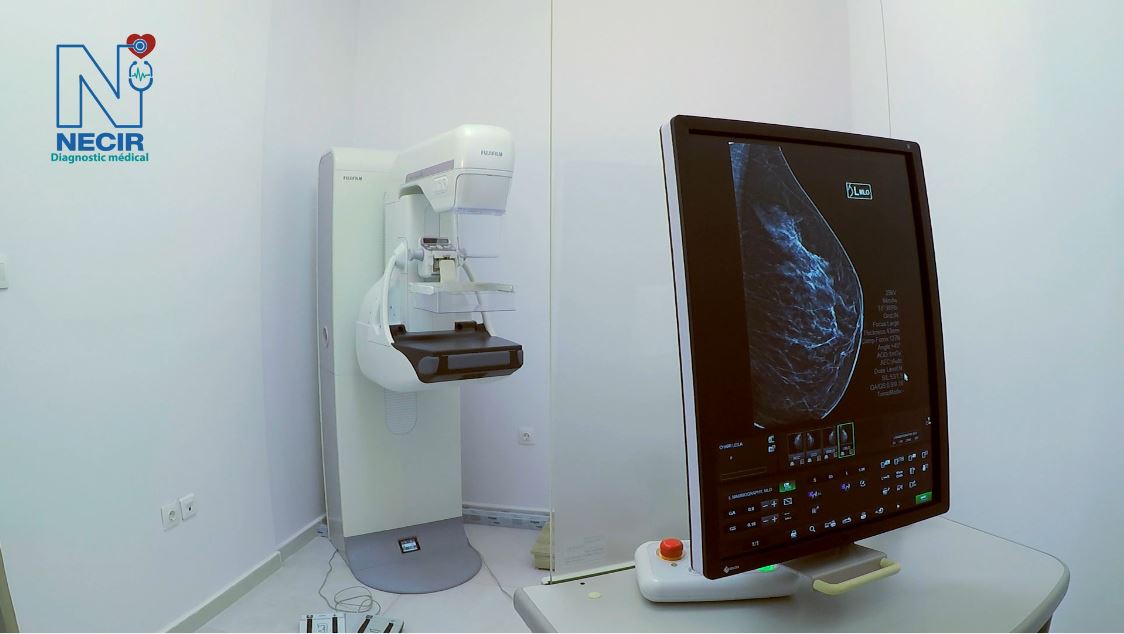
Mammography
The AMULET Innovality system integrates solutions that allow working on precision images combining Fujifilm’s advanced technologies, Dynamic Visualization II and Iterative Super Reconstruction, improving reading comfort and speed due to balanced image processing and display of all relevant details in one image.

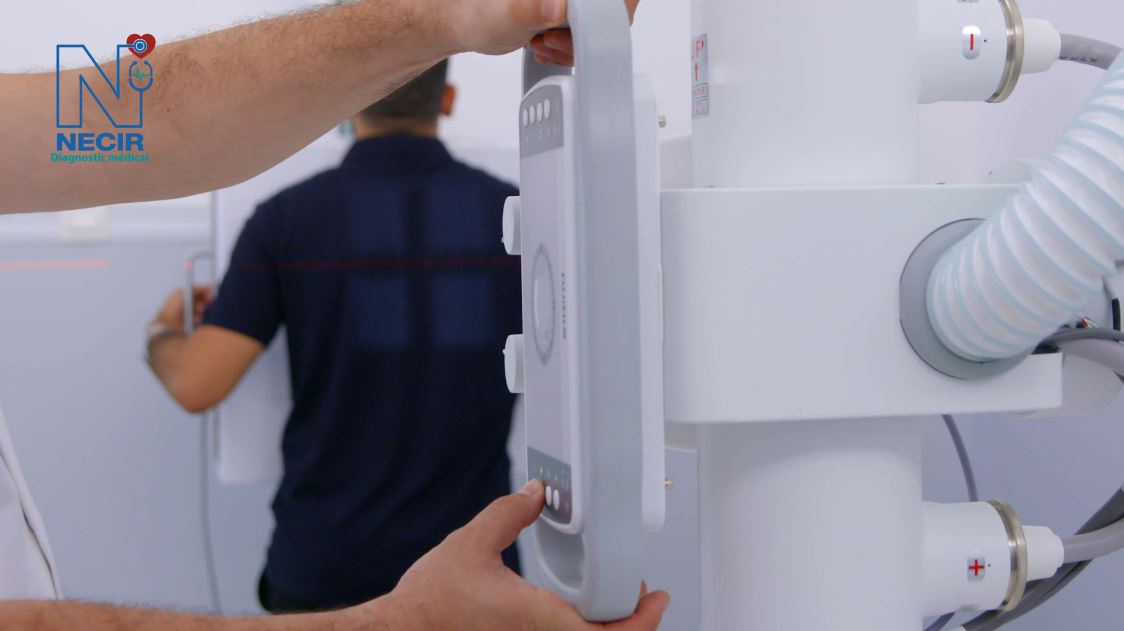
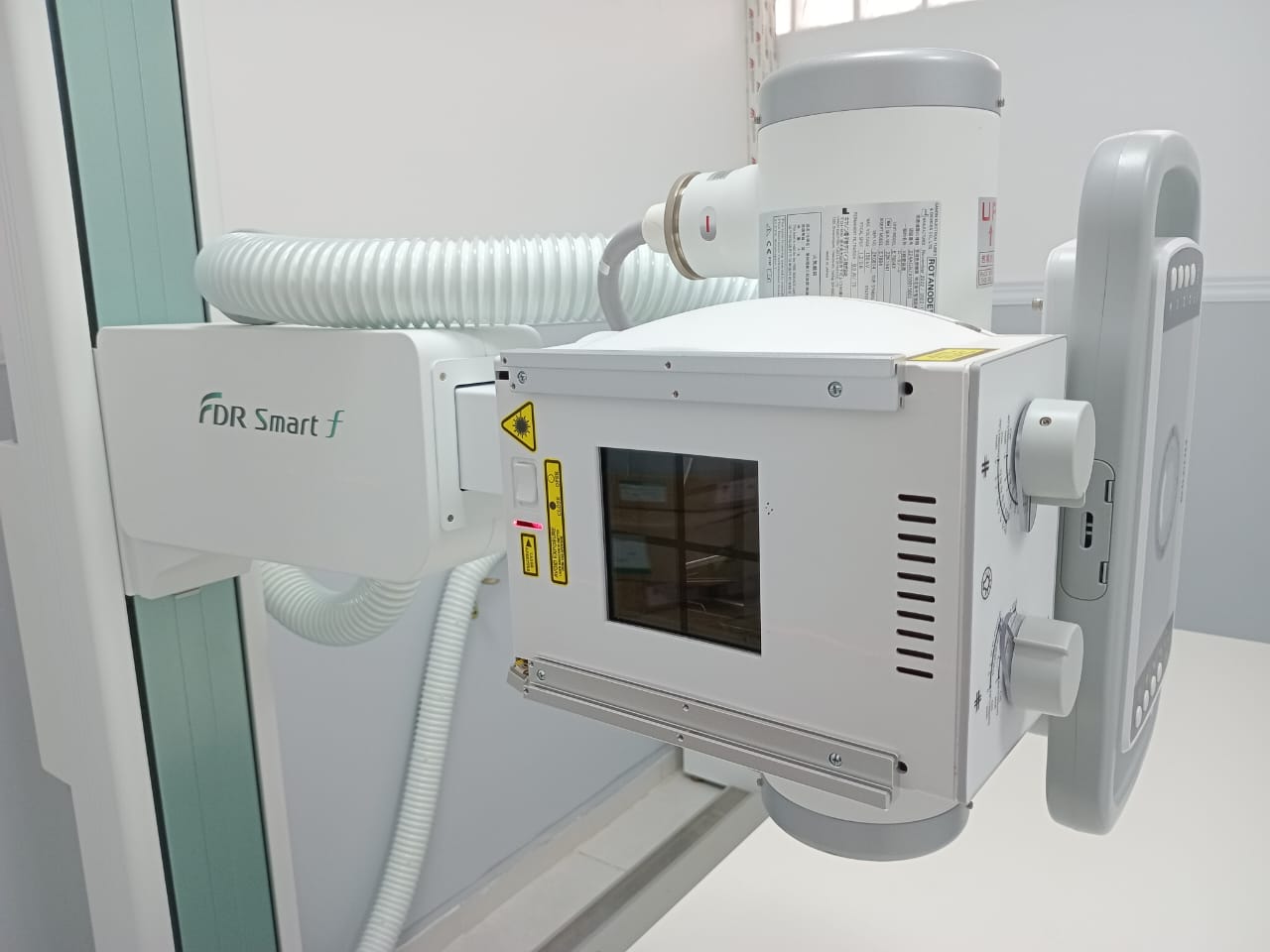
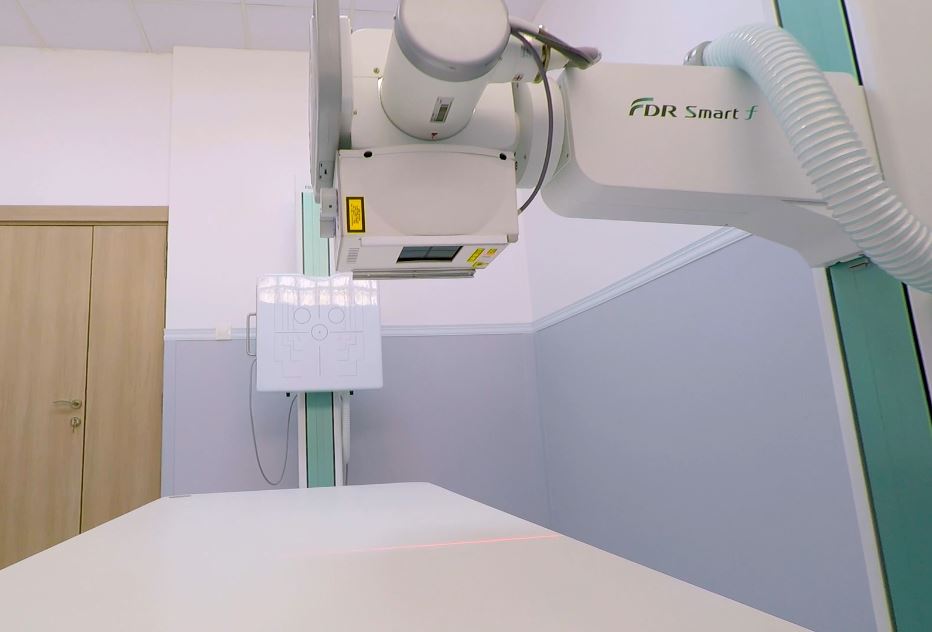
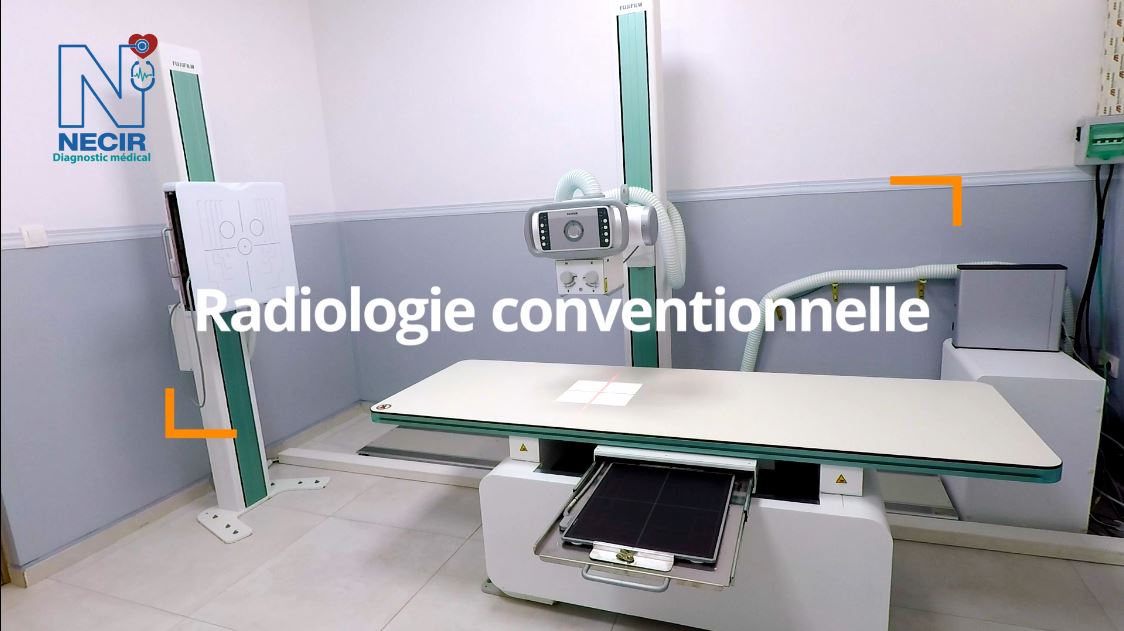
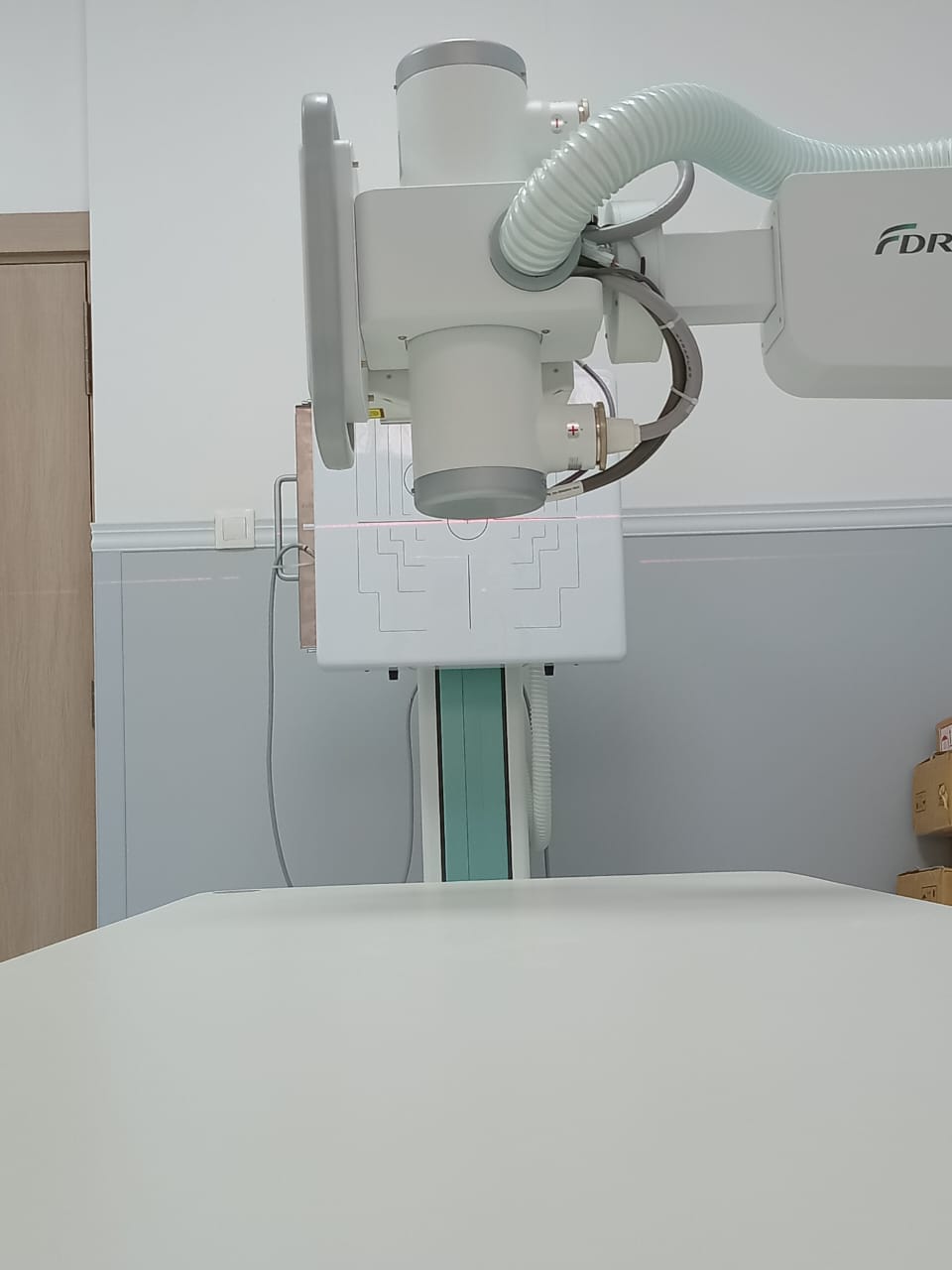
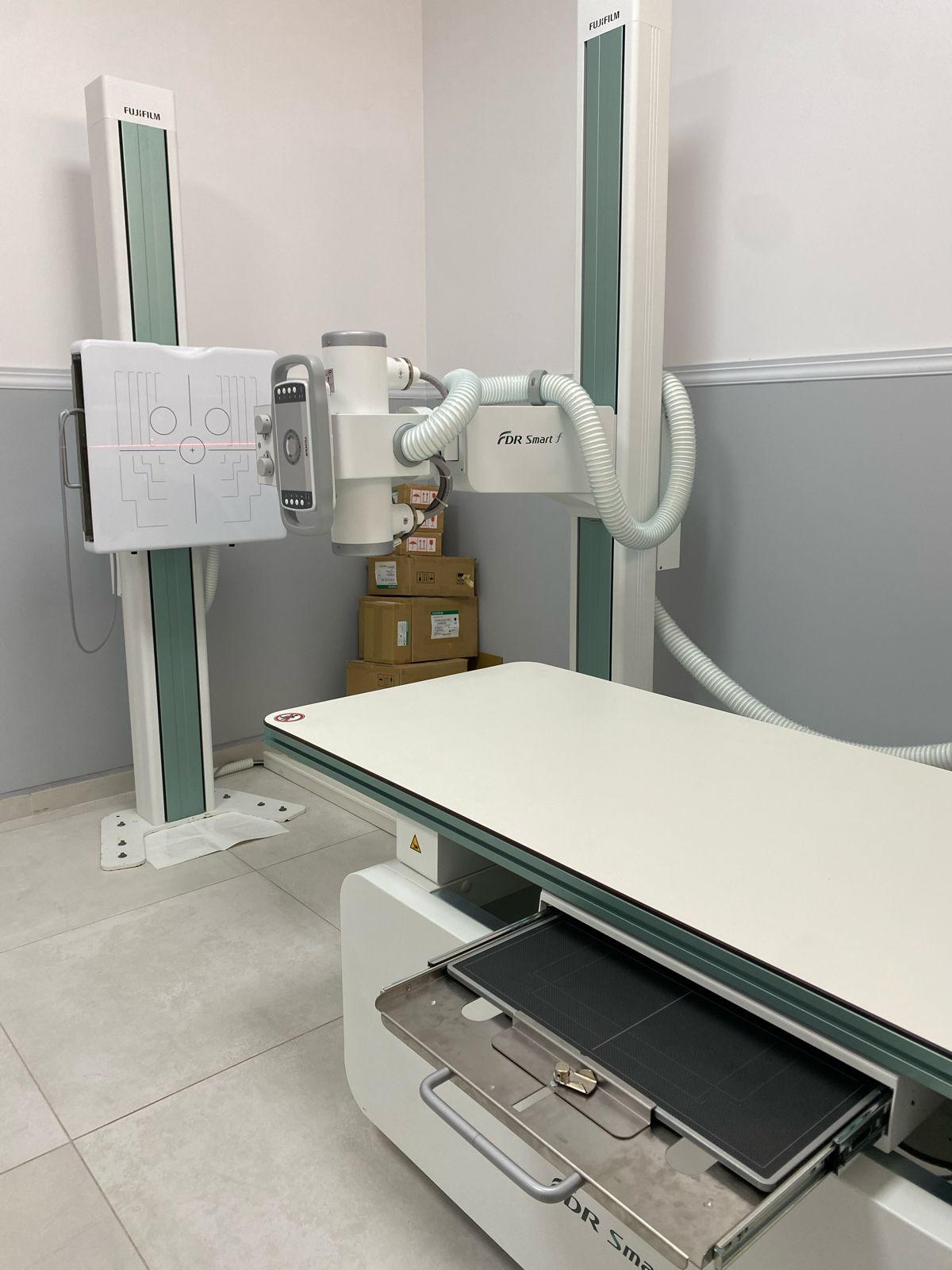
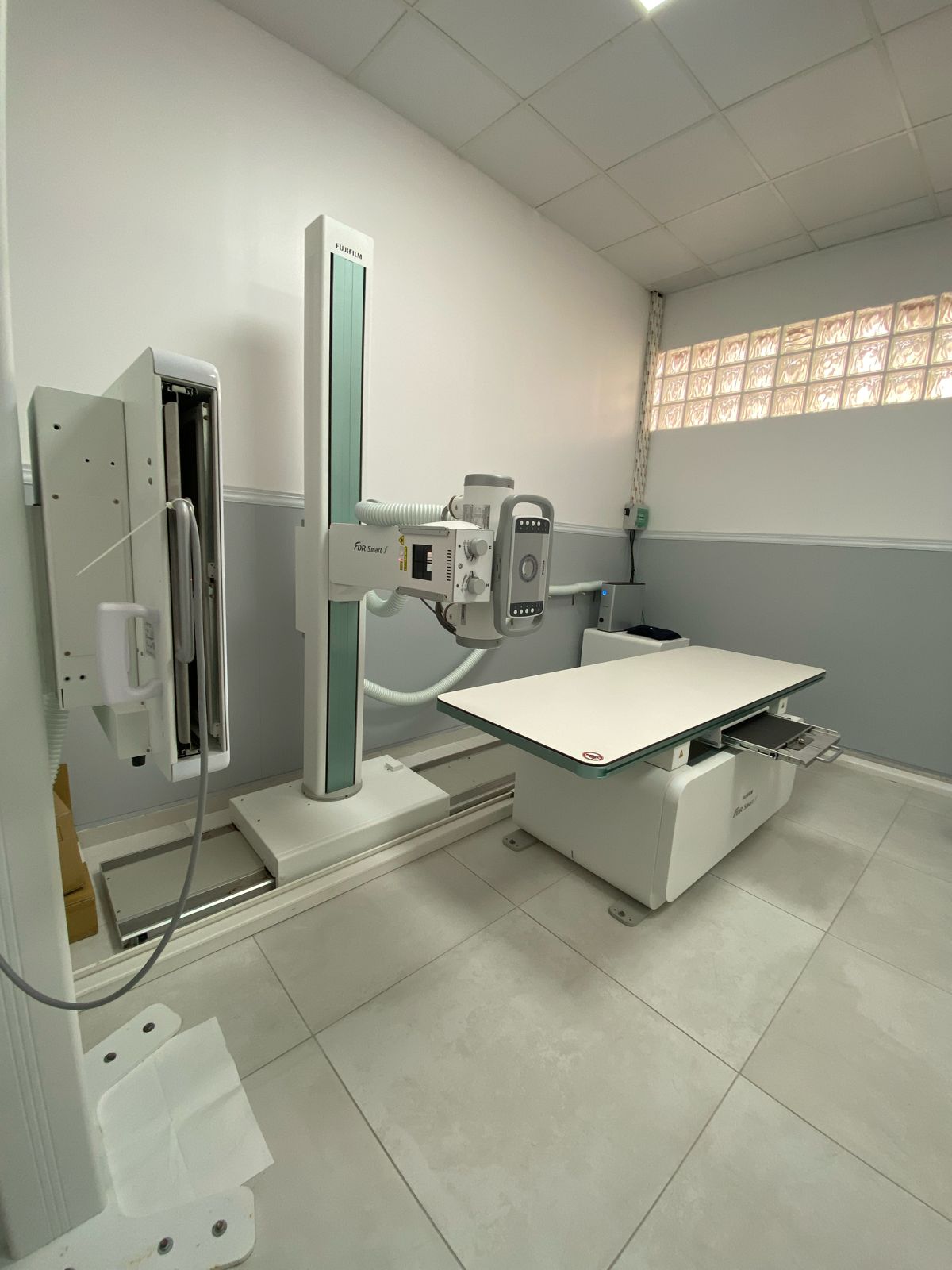
Conventional Radiology
The “FDR Smart f” table is equipped with the DR system for general radiography, which offers maintained image quality thanks to FUJIFILM’s “Image IntelligenceTM” technology, while its tilting vertical radiographic support allows great flexibility and facilitates examination for wheelchair users.

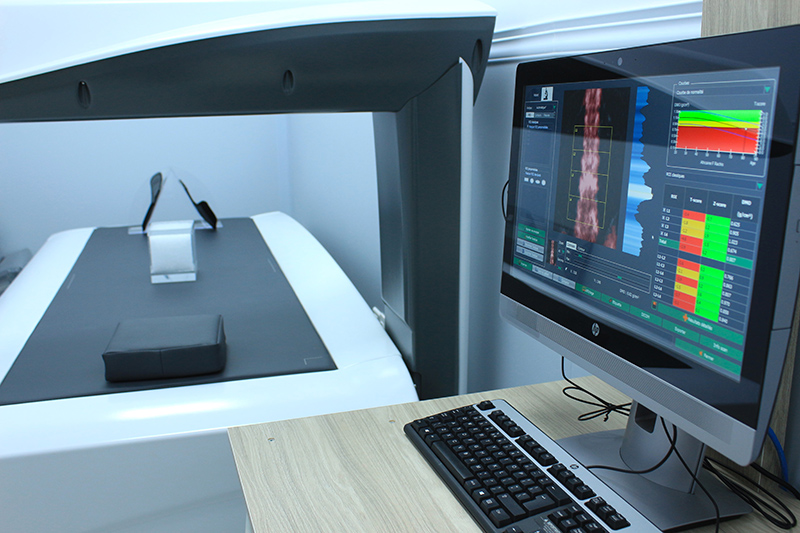
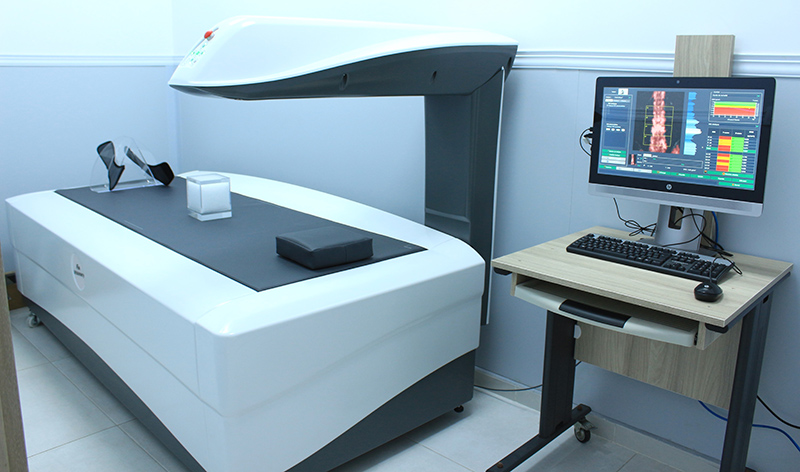
Bone mineral density (BMD)
The effective, powerful, and fast solution to assess bone structure and fracture risk, thanks to a large analysis surface. The results provide a wide range of information on the whole-body composition.
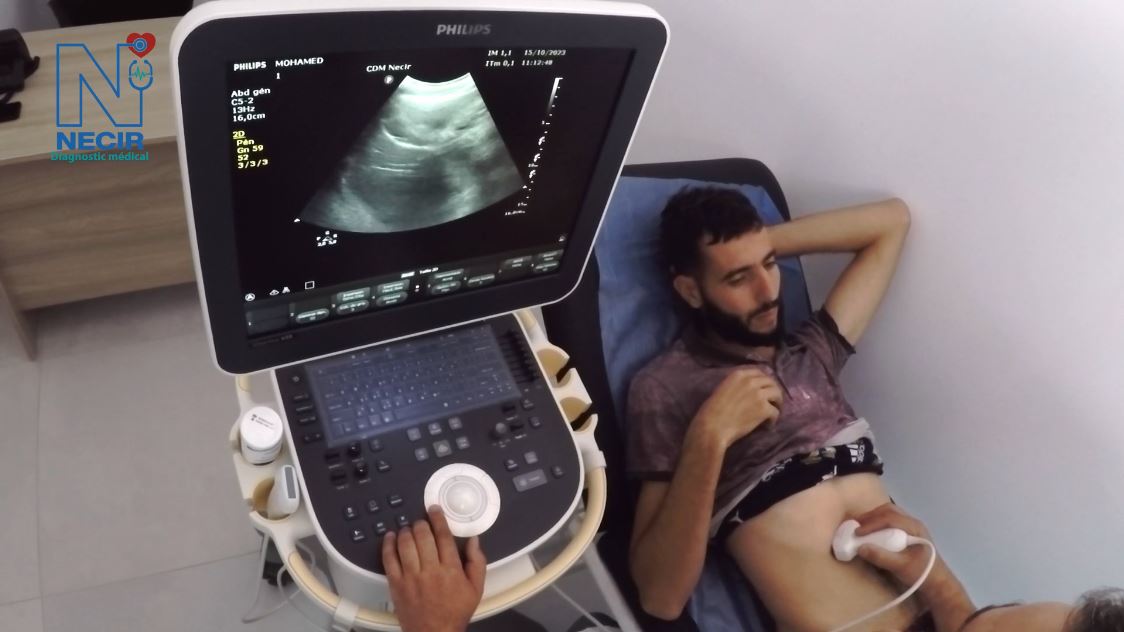
Doppler Ultrasound

Powerful and efficient, this system guarantees excellent images. By minimizing the workflow, this shared service ultrasound scanner offers a better penetration, with sensitivity and improved image uniformity.
Good to know!
MRI
What are the types of MRI examinations?
Chest, abdomen, and pelvis
Neurology or brain
Osteoarticular
Abdominal
Pelvic
Arthrography
ENT
Angiography with and without contrast
Whole body
How is the examination carried out?
Before the MRI examination, the patient is requested to undress and wear a gown, hairnet, and slippers. Injection of a contrast agent is generally necessary to enhance image clarity and readability.
During the examination
The patient lies on a table that slides into the tunnel. The examination lasts 30 to 60 minutes. MRI is a noisy method. Whenever possible, the patient is equipped with headphones playing self-selected music, except for brain MRI for which the patient is offered earplugs.
Contraindications
Absolute contraindications for MRI are: the presence of metal fragments in the eyeballs or a pacemaker. Patients with a heart valve or surgical clips for cerebral aneurysms must submit the model and number of their valve or clip, for verification of compatibility with MRI. Claustrophobia is a relative contraindication.
Good to know!
cCT canner
Types of scanner
Standard bone, abdominal, thoracic, neurological sequences
Virtual colonoscopy
Dentascanner.
+++
How does it work?
The scanner consists of a ring inside which is the X-ray tube that makes thin-section images. The X-ray tube rotates around the patient and the images are generated by a powerful computer system. In most cases, an iodine-based contrast agent is used to enhance their quality.
What are the risks associated with the scanner?
The scanner exposes the patient to a dose of X-rays higher than a standard X-ray. However, the risks associated with this irradiation are negligible. Some latest generation machines emit low irradiation, known as low dose.
Contraindications
Any allergy problems must be reported to your radiologist before undergoing the examination.